With the drastic changes to the climate, climate-concious engines such as PZEV are on a gradual rise in necessity. But with almost every eco-friendly alternative, there are a few features that make it distinct from the original.
So in order to cut down your carbon footprint, what are the compromises of using an eco-friendly PZEV engine?
Partial Zero Emissions Vehicles, or PZEVs, are vehicles that are designed to release a limited amount of threatening emissions into the atmosphere. These aren’t like regular engines, which is why there is so much speculation about their effectiveness.
In the following article, we’ll be going through all you need to know about the PZEV engine, including its key features, the difference between it and other engines, and its pros and cons.
What Is a PZEV Engine?
PZEV stands for Partial Zero Emissions Vehicle. After the implementation of California’s Clean Air Act of 2004, these engines were developed to combat the environmental crisis and reduce motor emissions in the atmosphere.
A PZEV includes gasoline engines and diesel engines. It also includes hybrid cars that release limited amounts of nitrogen oxides that can lead to smog formation. These engines are generally found in diesel engine cars, hybrid cars, or gasoline-electric cars.
A vehicle with a PZEV engine will work to reduce pollutant and evaporative emissions through a series of air-filtering processes. This ensures the waste gas contains as few harmful pollutants as possible.
How Does a PZEV Engine Work?
According to Subaru, a PZEV engine works by utilizing its four main components: the catalytic converter, fuel injectors, dual-filtration air-intake system, and the ECM (Engine Control Module).
Here are the roles of each of these key components –
Catalytic Converter
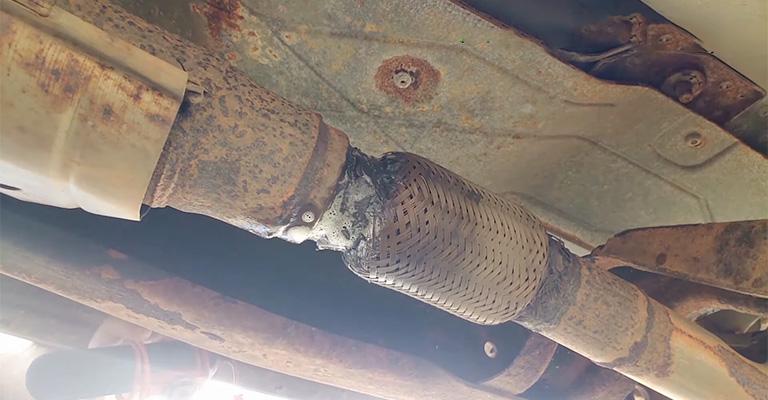

Catalysts lining the mesh of a PZEV’s catalytic converter change the molecular structure of the harmful emissions as they pass into the engine. This helps to significantly reduce about 90% of the pollutants into less-threatening gasses.
Fuel Injectors
The fuel injectors close tightly to guard the intake manifold from evaporative emissions entering it through fuel leakages. It also ‘injects’ fuel into the intake manifold, creating an air-fuel mixture that then becomes compressed in the combustion chamber; this powers the engine.
Dual-Filtration Air-Intake System
In regular cars, gasses that remain unburned can seep into the engine’s air intake as soon as it shuts off. This can possibly cause the engine to detonate. But with a PZEV engine, the charcoal canister in the air-intake filtration system readily absorbs evaporative hydrocarbon emissions.
ECM
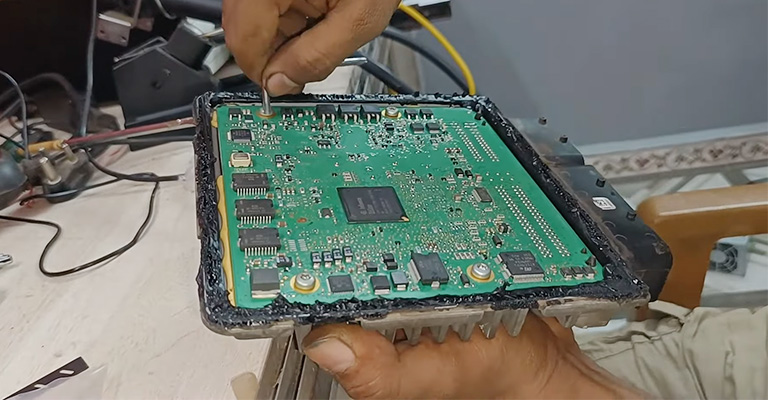

Cold starts can lead to horrible motor emissions. An ECM in a PZEV engine is designed to delay the ignition timing. This causes the exhaust gasses to heat up more and therefore helps the catalytic converter to start up faster. As a result, there’s a significant decrease in overall emissions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PZEV Engine
The advantages of having a PZEV engine include the following –
- Zero Production of Evaporative Emissions
With the engine’s anti-permeation fuel system liners, carbon air intake traps, and carbon canister scrubbers, there is no chance of evaporative emissions being produced, even though fuel leakages. This prevents incomplete combustion, which can possibly lead to engine detonation.
- Smog Reduction

The four main components of the PZEV engine, with additional adjustments to the overall system, allow for more than a 90% reduction in smog emissions. When smog is left in the air, it can cause acid rain as well as health issues, so this engine combats both problems by producing cleaner air.
Plus, a PZEV engine can also reduce the production of other harmful gasses which are usually emitted by standard cars, such as carbon monoxide, nitric oxide, nitrogen dioxide, and more.
- No Alternative Fuels Required
Alternative fuels are taken from sources apart from petroleum, which is why vehicle owners tend to use them in place of petroleum products. However, since PZEVs are already gas-powered, they do not require any alternative fuels.
Burning natural gas in place of petroleum results in fewer emissions of harmful air pollutants, especially carbon dioxide.
- Easy Maintenance and Repair

PZEV engines are surprisingly more easy to maintain and get fixed than standard engines. They don’t include any intricate or costly technology, so they can be repaired at most shops.
They can also be easy to have replaced, as they have warranties for certain emission control parts that can last up to 15 years.
However, PZEVs can also come with their own set of disadvantages, such as –
- Low Carbon Dioxide Reduction
PZEV engines do wonders for reducing pollutants in the waste air of your car and produce cleaner air that prevents smog formation. But this does not mean that they also totally prevent carbon dioxide emissions, and neither do they improve the efficiency of fuel usage.
- Reduced Fuel Economy

PZEV engines are also known to have slightly low fuel efficiency compared to standard engines. This is due to the extra components inside the engine, which require more energy from fuel in order to work.
Difference Between ULEV, ZEV, and PZEV Engines
PZEV is not the only type of low-emission engine available in the market; there are also other types, including SULEV, LEV, ULEV, and ZEV. For this section, we’re going to use ULEV and ZEV as examples to help you distinguish PZEV from other low-emission engines.
The differences between ULEV and PZEV engines are –
- PZEV means partial zero-emissions, ULEV means ultra-low-emissions
- PZEV produce fewer pollutants than ULEVs
- PZEV produce fewer hydrocarbons and carbon dioxide than ULEVs
- Both PZEV and ULEV reduce smog-forming pollutants from waste gasses
- PZEV produces zero evaporative emissions, and ULEV produces a few
The differences between ZEV and PZEV engines are –
- PZEV stands for partial zero-emissions, and ZEV means zero-emissions
- ZEV is battery electric or fuel cell electric; PZEV is a gas-powered engine
- Both produce reduced emissions for certain pollutants, clearing waste gasses
- PZEVs produce certain emissions at a low level; ZEVs produce zero emissions for all pollutants
- PZEVs are designed to meet the emission standards of a ZEV
Frequently Asked Questions
Does PZEV affect gas mileage?
Yes, it can affect gas mileage, as PZEVs are known to have a low fuel economy. They use more energy from fuel to power the extra components found in their engine to aid in filtering emissions. As a result, more fuel is consumed to keep the engine running smoothly.
Does PZEV cost more?
PZEV can be costly when it comes to the installation of a new model, so they are considered more expensive than a standard engine. But PZEVs cost much less than a standard engine in terms of maintenance, repair, and replacements.
What are at-PZEVs?
AT-PZEVs, better known as Advanced Technology PZEVs, are similar to PZEVs. But, they exceed the regular PZEV standards and apply to plug-in hybrid electric and/or hydrogen vehicles.
What does it mean when a PZEV engine has no emissions?
It means that the vehicle itself does not emit exhaust gas or other harmful pollutants through the engine and into the air.
Conclusion
Overall, a PZEV engine is a very effective way to reduce threatening emissions caused by combustion. Plus, it comes with incentives such as warranties for certain parts and easy replacement services that standard vehicles don’t have.
If you’re looking for a more eco-conscious way of traveling, then a PZEV is a great way to start.
Leave a Reply