A series of intake and exhaust valves are placed on the cylinder head of your car engine to allow airflow in and out of the cylinders. The valves are essential parts of the system as the passing air ignites the fuel and starts the car.
If your engine valves are burnt because of excessive heat, the cylinders won’t be sealed properly, causing a loss of power and compression. As a result, your car will show various symptoms of burnt valves.
Rough idling, increased fuel consumption, engine misfiring, loud noises from the cylinder, reduced engine power, difficulty starting, air leaks, activated check engine light, failed emission test, etc., are the common symptoms of burnt engine valves.
Let’s explore the signs of a burnt valve and find out the causes and some easy fixes in upcoming sections.
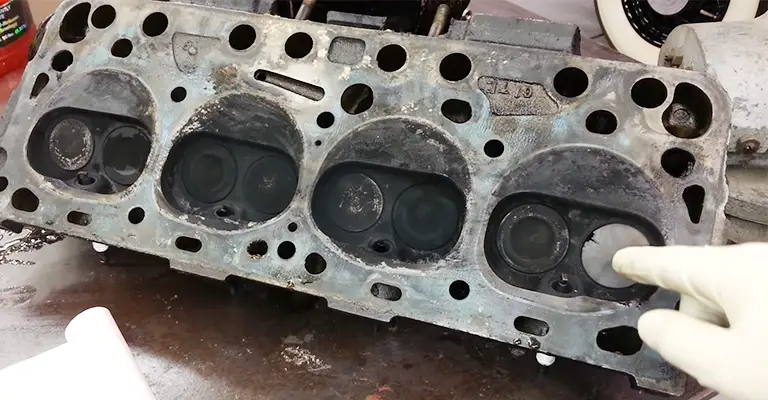

Burnt Engine Valves: Symptoms and Causes
On the top of each engine cylinder, you’ll find four (or two) engine valves. Two of them are the intake valves that allow cool air inside the cylinder. The remaining two are the exhaust valves that exhaust the hot air from the cylinder.
As the engine valves are constantly subjected to high temperatures (1200-1350 degrees Fahrenheit), the valve edges often get burned. In some cases, the whole valve gets damaged due to thermal shock.
Here are the most common symptoms and possible causes of burnt valves:
Engine Misfiring
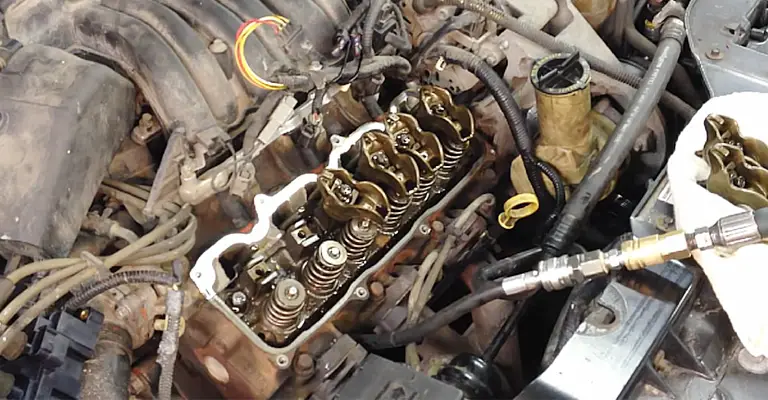

When a valve is burned, it can’t provide sealing for the cylinder. As a result, the engine misfires and stalls when you start the vehicle. Also, your car engine and steering wheel might vibrate, indicating a burned valve.
Now, the engine can misfire for various other reasons related to the engine components. So, you need to do a compression test to make sure a burnt valve is the root of this problem.
What’s the Cause?
Adequate compression and the proper mix of air and fuel are essential for engine combustion. If your engine has a burnt valve, it can’t seal properly, causing a loss of air-fuel mixture and compression. Hence, the engine doesn’t get enough power to start the car and misfires.
Increased Fuel Consumption

Burnt valves directly affect your engine performance and make it work more than regular. As a result, the engine uses more fuel to compensate for the lack of compression inside the cylinders.
Therefore, if there’s a burnt valve, you’ll have to refill your vehicle more often because of the increased fuel consumption.
What’s the Cause?
As mentioned, burnt valves cause a loss in compression inside the engine cylinders. This leads to bad performance for many of the engine components. To keep the combustion chamber running, your car uses extra fuel, increasing gas mileage.
Rough Idling
Over time, the valve seat and the valve body wear out due to mechanical pressure and heat production. A worn-out valve won’t seat properly on the cylinder head letting hot gases out. Hence, the valve gets burnt, and you experience rough idling.
What’s the Cause?
Apart from regular wear, there are some other reasons why the valve doesn’t seat properly on the cylinder head. Incorrect adjustment of the lash, carbon buildup, malfunctioning valve spring, etc., also causes the valve to become loose and prevents it from sealing the cylinder head.
Reduced Engine Power

When there’s a burnt valve in your car, your engine power will keep reducing no matter what you do. In fact, the engine power can decrease by up to 25% in some cases.
What’s the Cause?
In this case, the lack of fuel is to blame. Without sufficient fuel, the exhaust gas temperature will increase, and the level of oxygen and nitric oxide will also go high.
As oxygen is combustible, it further contributes to the temperature rise. Consequently, excessive heat production damages the valves and reduces engine power.
Check Engine Light Turned On
As we have learned, burnt engine valves lead to a number of engine issues. Your vehicle has sensors in different engine parts that send signals to the Engine Control Module (ECU) or the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) when any engine malfunction is detected.
As a result, the check engine light will turn on, and you’ll get a trouble code indicating the damaged engine component.
What’s the Cause?
High operating temperatures are the key reason for burnt valves and damaged engine parts. When the cooling system of your car fails, the produced heat remains trapped inside the car engine, causing the engine to misfire and trigger the check engine light.
Air Leaks
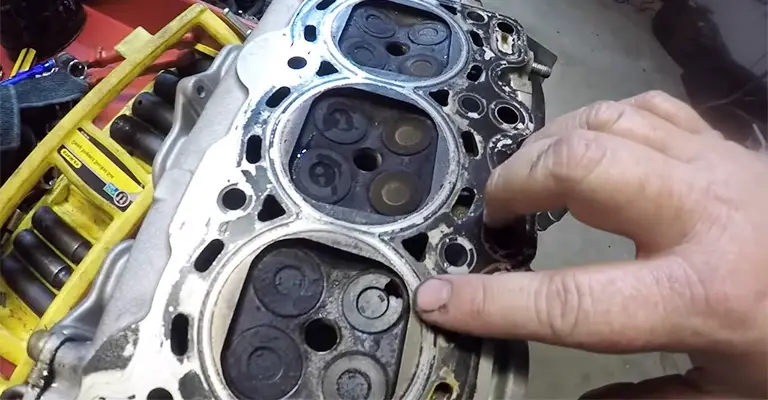
If your car has a burnt valve, you’ll notice air-leaking noises from different parts of the transmission. Typically, the air will escape through the exhaust pipes for burnt exhaust valves.
On the other hand, you’ll hear air escaping noises from the throttle body or intake manifold if the intake valves are burnt. A leak test will reveal the burnt valve, and you’ll only need an air compressor to conduct the test.
What’s the Cause?
As you know, burnt valves don’t provide adequate sealing for the cylinders. Hence, air leaks through the damaged valve creating escaping noises along the way.
Difficulty in Starting and Engine Noises
The engine cylinders are essential to start the engine, so burnt valves will directly affect the engine’s performance. With a damaged valve, cold starts will be difficult, and your engine will make unusual noises while starting and gear shifting.
What’s the Cause?
Your engine needs a proper mix of air and fuel for combustion. Burnt valves don’t provide a sufficient amount of air to fire up the engine. Hence, the engine can’t function optimally even when the cylinders are perfectly fine.
Final Words
So, now you know all the common symptoms of burnt valves. As we have discussed, most signs are related to the engine and cylinder performance.
Also, symptoms like rough idling, difficulty starting, engine noises, etc., are pretty common for many other engine issues. So, you need to visually inspect the valves or conduct a leak test to make sure there’s a burnt valve somewhere on the cylinders.
Leave a Reply