You probably won’t realize how important your car battery is until it dies and becomes a pain in the neck. Sure, a jump-start can get the engine running but is that a permanent fix though? It’s very important to charge your car battery. But how long should you charge it is just as important if not more.
So how long does it take to charge a car battery? Well, it depends on the method as well as the remaining amps in the battery. To know that you’ll have to learn some basics about batteries, let’s hop into that first.

How Many Amps Is a Car Battery?
A car battery can put out up to 1000 amps in a short amount of time. However, it can vary quite a bit. Usually, in car batteries, it’s between 550 and 1000 amperes depending on the type and size.

What are the Ampere Ratings
Ampere rating or amp rating is an electrical current value given to each fuse. This is the sustainable amount of current which can flow continuously through a fuse under specific conditions. In the case of batteries, the ampere ratings tell you the electrical storage capacity of them.
Cranking Amperes (CA) and Cold Cranking Amperes (CCA) are two of the most important ampere ratings you’d want to look out for when it comes to car battery performance. The CA rating is higher than the CCA rating most of the time.
CA
The Cranking Ampere (CA) rating is the amount of current the battery provides for the car engine to start at 32 degrees Fahrenheit for 30 seconds at 1.2 Voltage for every battery cell. This basically indicates the capability of a car battery to power your car engine at normal temperature.
CCA
The Cold Cranking Ampere (CCA) on the other hand is the current the battery gives to the car engine for 30 seconds at 1.2 volts for each cell at -4 degrees Fahrenheit. Simply put, it’s the amount of power car battery can provide to start the engine during winter.
If you’re trying to figure out how many amps your car battery puts out, you need to pay close attention to the Cold Cranking Ampere (CCA) rating. This is the power you’ll get from the battery in more demanding situations and so, is a much accurate depiction of the battery’s ability.
Factors Affecting Amperage of Battery
Mostly these are the internal constructional factors that grab an influence on the battery amperage. Yet the environmental aspects impose affluently too.
Surface Area of The Plates
Most car batteries are lead-acid batteries. These types of batteries contain series-strings of lead-acid cells where the negative plate is lead and the positive one is lead dioxide in each cell while fully charged. Sulphuric acid works as an electrolyte.
During discharge, a chemical process results in both plates becoming covered with lead-sulfate and the electrolyte changing into water. While charging, this process is reversed and energy is stored in the cells once again.
The capacity of the battery largely depends on the surface area of the plates where the chemical reactions take place.

Temperature
Temperature is another key factor that affects energy storage as well as battery life. The conductivity of the cell plates and electrolyte decreases at low temperatures. So, the increase in temperature results in a higher effective capacity.
The Rate of Discharge
The rate of discharge also governs the effective capacity. A slower rate of discharge results in a higher effective capacity. Deep discharges cause the battery to not get fully charged and lose its charge more easily.
Age of The Battery
The capacity of any battery diminishes with age as well. Damage from heat and vibration coupled with standard wear and tear reduces its storage capacity. Most batteries need to be replaced between 5-7 years.

Car Battery Amp-hour Chart
A battery with a capacity of 1 Amp-hour of Ah should supply current of 1 Amp to a load for 1 hour or half Amps for 2 hours before being discharged. That sounds pretty simple, right? Well, it’s a bit more complicated than that.
In an ideal case, the relation between the current provided by the battery and the time to discharge may be absolute, but real batteries don’t actually follow this linear relation.
That’s why battery manufacturers use 10-hour rates or even 20 or 100 to calculate capacity meaning it takes that amount of time for the battery to discharge completely.
An average car battery has a capacity of about 48 Ah. Which means it can provide around 4 Amps for 10 hours before discharge. One thing to keep in mind is that the more current you draw, the more you lower the capacity of the battery.
Let’s say a battery has a capacity of 200Ah and it can provide 10 Amps for 20 hours. You may think that this battery can also provide 50 Amps for 4 hours, right? Well, that’s not the case as we can see from the chart below.
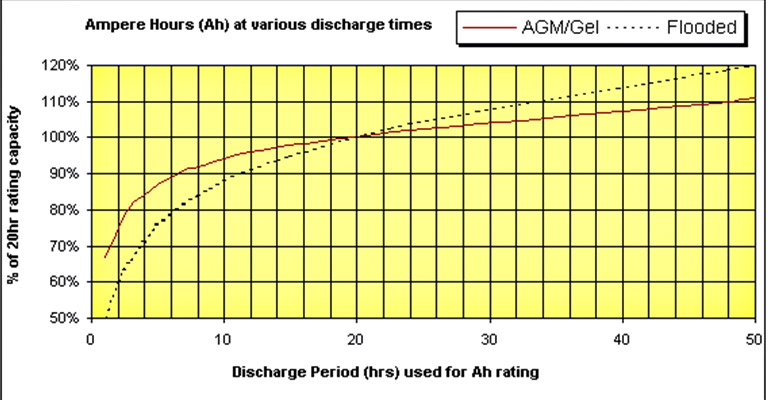
Discharge period used for Ah rating
Credit: tuningenmedellin.blogspot.com
From the chart, you can see that the 4-hour line intersects the flooded line close to 70% battery capacity. Basically, it means the capacity of the battery will be 140 Ah. So, if you try to draw 50 Amps from a 200 Ah battery of 20 hour-rate, you will get around 35 Amp for 4 hours before it completely discharges.
Conclusion
So, if you’ve ever wondered how many amps your car battery puts outs, you need to check a couple of things. Usually, that number is between 550 and 1000. It depends on the type of car you own and the size of the battery.
Ampere ratings can give you a clear indication of the capabilities of your car battery, especially the Cold Cranking Ampere (CCA) rating. However, some factors such as the surface area of the plates, temperature, usage will vary the effective capacity.
Also read – How Long Should it Take to Charge a Car Battery?
Leave a Reply